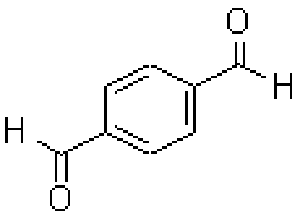
1,4-Phthalaldehyde
Structural formula
Chemical Name: 1,4-Phthalaldehyde,
Other Names: Terephthaldicarboxaldehyde, 1,4-Benzenedicarboxaldehyde
Formula: C8H6O2
Molecular Weight:134.13
CAS No.: 623-27-8
EINECS: 210-784-8
Specifications
Appearance: white acicular crystal
Density: 1.189g/cm3
Melting point: 114~116℃
Boiling point: 245~248℃
Flash point: 76℃
Vapor pressure:0.027mmHg at 25℃
Solubility: easily soluble in alcohol, soluble in ether and hot water.
Production method
Add 6.0 g of sodium sulfide, 2.7 g of sulfur powder, 5 g of sodium hydroxide and 60 ml of water into a 250 ml three necked flask with reflux condenser and stirring device, and raise the temperature to 80 ℃ under stirring. The Yellow sulfur powder dissolves, and the solution turns red. After refluxing for 1 h, dark red sodium polysulfide solution is obtained.
Add 13.7 g of p-nitrotoluene, 80 ml of industrial ethanol, 0.279 g of N, N-dimethylformamide and 2.0 g of urea into a 250 ml three necked flask with a dropping funnel, a reflux condenser and a stirring device, heat and stir to dissolve p-nitrotoluene to obtain a light yellow solution. When the temperature is gradually raised to 80 ℃ and kept constant, the sodium polysulfide solution prepared in the above step is dropped, and the solution quickly turns blue, then turns dark green to dark brown, and finally turns reddish brown. It is dropped within 1.5-2.0 hours, and then kept at 80 ℃ for refluxing reaction for 2 hours. Steam distillation is carried out rapidly. At the same time of distillation, 100 ml water is added, 150 ml of distillate is collected, and pH value is 7. The residual liquid is cooled with ice quickly to precipitate light yellow crystals, which are extracted with ether (30 ml × 5), evaporated and dried to obtain p-aminobenzaldehyde yellow solid.
Add 5.89 paraformaldehyde, 13.2 g hydroxylamine hydrochloride and 85 ml water into a 250 ml three necked flask, heat and stir to make them all dissolve to obtain a colorless solution, then add 25.5 g sodium acetate hydrate, keep temperature at 80 ℃ and reflux for 15 min to obtain formaldehyde oxime (10%) colorless solution.
In a 50 ml beaker, add 3.5 g p-aminobenzaldehyde, 10 ml water, drop 5 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid, and keep stirring. The light yellow substance turns black quickly and dissolves continuously. It can be properly heated (below 6 ℃) to dissolve all of it. Cool it in ice salt bath, and the temperature drops to below 5 ℃. At this time, p-aminobenzaldehyde hydrochloride precipitates as fine particles, and the solution becomes paste. Under stirring, 5-10 ℃ 5 ml of sodium nitrite solution was dripped within 20 min, and the stirring was continued for about 20 min. 40% sodium acetate solution was used to adjust the Congo red test paper to be neutral to obtain diazonium salt solution.
Dissolve 0.7 g of crystalline copper sulfate, 0.2 g of sodium sulfite and 1.6 g of sodium acetate hydrate into 10% formaldehyde oxime solution, and the solution turns green. After dripping, keep the low temperature for 30 min to get a gray solution, add 30 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid, raise the temperature to 100 ℃, refluxe for 1 hour, the solution appears orange, steam distillation, get a white slightly yellow solid, filter and dry to get the crude product of p-benzaldehyde. The product was recrystallized with the mixed solvent of 1:1 alcohol and water.
Application
1,4-Phthalaldehyde is mainly used in dyestuff, fluorescent whitening agent, pharmacy, perfume and other industries. It is an important raw material for organic synthesis and fine chemical industry. At the same time, with two active aldehyde groups, it can not only self polymerize, but also copolymerize with other monomers to form polymer compounds with various properties. Thus makes it an important monomer for the synthesis of polymer materials.








